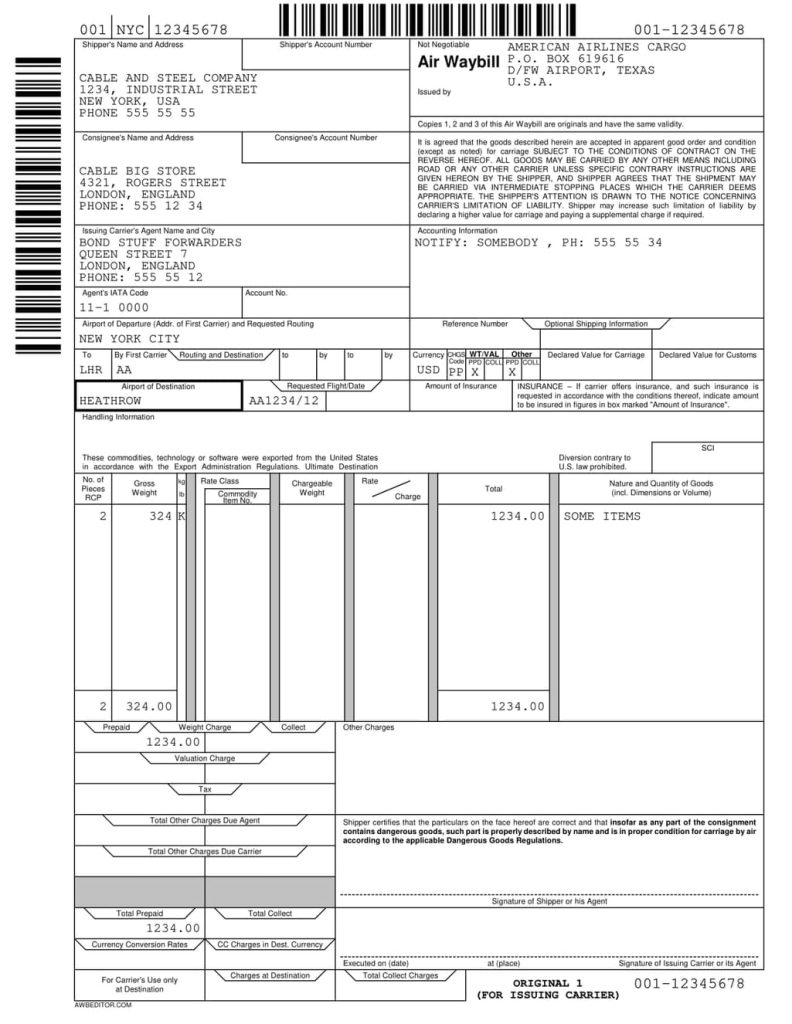
Basic information about Air Waybill (AWB)
An air waybill or air consignment note is a receipt issued by an international airline for goods and an evidence of the contract of carriage. It is not a document of title to the goods. The air waybill is non-negotiable.
Purpose and Function:
- An AWB accompanies goods shipped by an international air courier.
- It serves as a receipt of goods by the airline (carrier) and a contract of carriage between the shipper (sender) and the carrier.
- This legal agreement becomes enforceable when both the shipper (or their agent) and the carrier (or their agent) sign the document.
Key Information on an AWB:
- Standard Form: The AWB follows a standard format provided by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- Contents:
- Shipper’s name and address.
- Consignee’s name and address.
- Three-letter origin airport code.
- Three-letter destination airport code.
- Declared shipment value for customs.
- Number of pieces.
- Gross weight.
- Description of the goods.
- Any special instructions (e.g., “perishable”).
- Conditions of the contract, including liability limits and claims procedures.
- Applicable charges.
Non-Negotiable Instrument:
- Unlike other bills of lading, an AWB is non-negotiable.
- It does not specify the exact flight or arrival time.
- AWBs are issued in non-negotiable form, providing less protection compared to bills of lading.
Comparison with Bill of Lading:
- Bill of Lading: Legal document for goods carried by sea, specifying type, quantity, and destination.
- AWB: Contract solely for transportation, not covering merchandise value.
- AWBs are essential for tracking and identification during air shipments.
Filling out
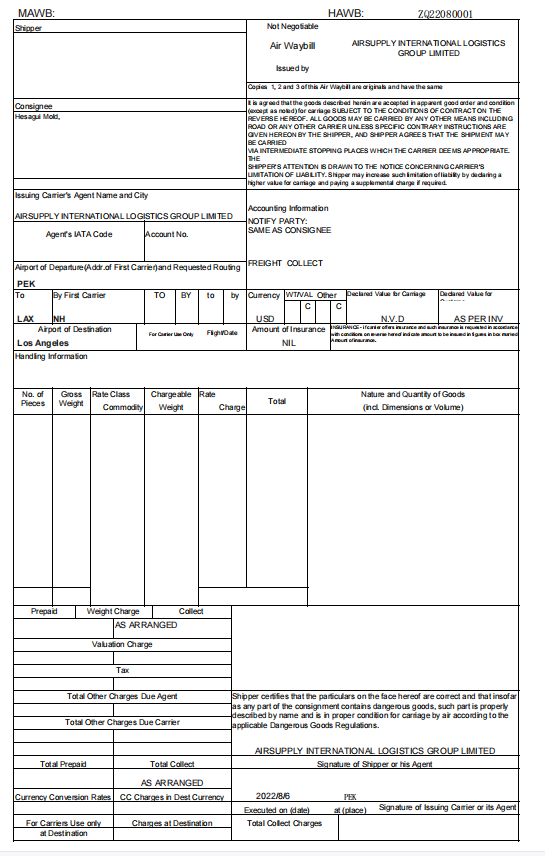
Your Details:
- Date: Mention the date when you’re filling out the AWB.
- Account Number: If applicable, include your account number with the carrier.
- Company Name: Clearly state your business name.
- Phone Number: Provide a contact number.
- Complete Address: Include your full address.
- VAT or Tax ID: If relevant, add your VAT or tax identification number.
- If there’s a different collection address, make sure to include it.
Receiver’s Details:
- Name: Specify the recipient’s name.
- Phone Number: Provide their contact number.
- Tax ID Number: If applicable, include the receiver’s tax identification number.
- Again, if there’s a different delivery address, ensure it’s included along with the contact details. Some countries accept post office addresses.
Shipment Details:
- Number of Packages: Indicate how many packages you’re shipping.
- Type of Package: Describe the type of packaging (e.g., boxes, crates).
- Weight and Dimensions: Provide accurate weight and dimensions for each package.
- For international shipments, include:
- Goods Description: Briefly describe the items being shipped.
- Value: Specify the value of the goods.
- HS Code: Assign the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for customs classification.
- If you’re shipping dangerous goods, declare this information.
Select a Shipping Service:
- Choose from available options such as next-day delivery, early-morning delivery, or Saturday service.
Billing Section:
- Clarify who is paying the carrier freight charges:
- If you’re handling payment, add your account number.
- If the receiver is paying, include their account number (with their permission).
Sign It:
- Either you or a company representative must sign the AWB.
Additional Consideration:
- Include a packing list inside the package with a detailed goods description.
Read more:
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT COMMERCIAL INVOICE