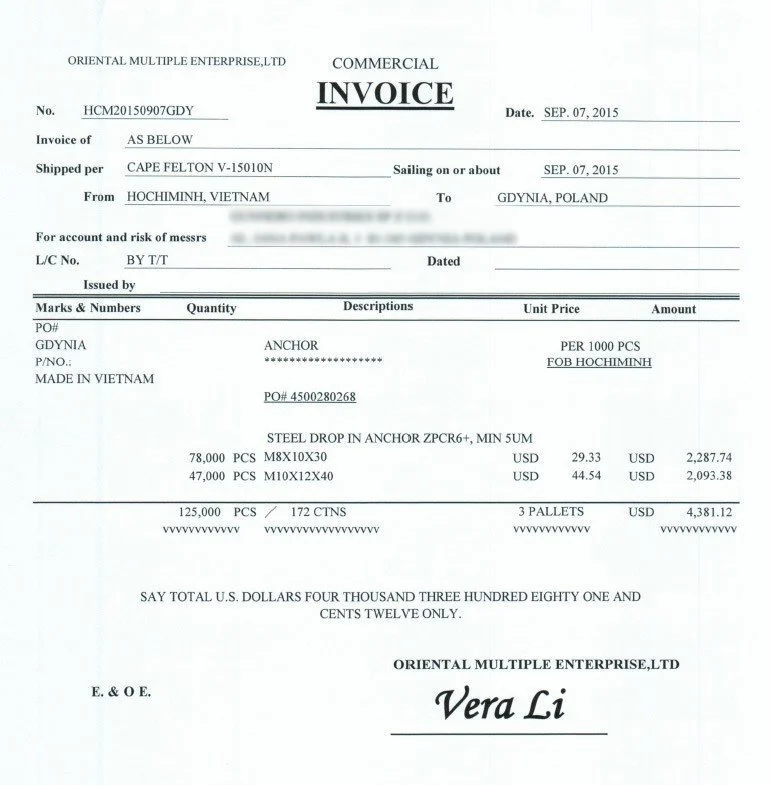
Basic information about Commercial Invoice
A commercial invoice is a crucial document used in international trade. A commercial invoice is a required document for the export and import clearance process. It is sometimes used for foreign exchange purposes.
Purpose and Importance:
- A commercial invoice serves as a request for payment for goods sold internationally.
- It is required by customs to determine applicable taxes, tariffs, or duties for imported goods.
- Customs authorities use it to prevent any delays during the import process.
When Is It Required?
- A commercial invoice is mandatory for shipments across international borders.
- For example, when shipping from the US to Canada, the US to the EU, or any other international destination, you must attach a commercial invoice.
Key Elements of a Commercial Invoice:
- Header: Includes contact information for both the buyer (importer) and the seller (exporter).
- Product Details:
- Country of Origin: Where the goods were manufactured or produced.
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: A standardized code that classifies products for customs purposes.
- Product List: Describes the items being shipped.
- Payment Terms: Specifies how and when payment is expected.
- Freight Terms: Details the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Other Relevant Information: Any additional details necessary for customs clearance.
Proforma Invoice vs Commercial Invoice:
- Before issuing a commercial invoice, businesses often send a proforma invoice.
- The proforma invoice provides the buyer with an estimate of the final invoice cost and delivery timing.
- Unlike the commercial invoice, the proforma invoice does not serve as a request for payment.
How to create one

Header Information:
- Start by including your company’s details (the seller/exporter) and the recipient’s details (the buyer/importer). Include the following:
- Your Company Name and Address: Clearly state your business name, address, and contact information.
- Buyer’s Company Name and Address: Include the recipient’s company name, address, and contact details.
Invoice Number and Date:
- Assign a unique invoice number to this transaction.
- Specify the date when the invoice was issued.
Product Details:
- List the items being shipped. Include the following for each product:
- Description: A brief description of the product.
- Quantity: The number of units being shipped.
- Unit Price: The price per unit.
- Total Price: Multiply the quantity by the unit price to calculate the total cost for each item.
Currency and Payment Terms:
- Indicate the currency in which the transaction is conducted (e.g., USD, EUR, JPY).
- Clearly state the payment terms (e.g., “Payment due within 30 days from the invoice date”).
Shipping and Freight Details:
- Specify the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Include any freight charges or shipping costs.
Country of Origin and HS Code:
- Mention the country where the goods were manufactured or produced.
- Assign the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for each product. This code helps customs classify the goods.
Additional Notes:
Add any relevant information, such as special instructions, terms, or conditions.
Sign and Date:
- Sign the invoice to validate it.
- Include the date of issuance.
It’s also important to keep copies of your commercial invoices for your records and for customs purposes.
You might also be interested in: