Basic information about GMP Standard
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practice, and it refers to a set of quality control standards and guidelines established by regulatory agencies to ensure the consistent production of safe, high-quality products. GMP standard is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, cosmetics, dietary supplements, and medical devices, where product quality and safety are paramount.
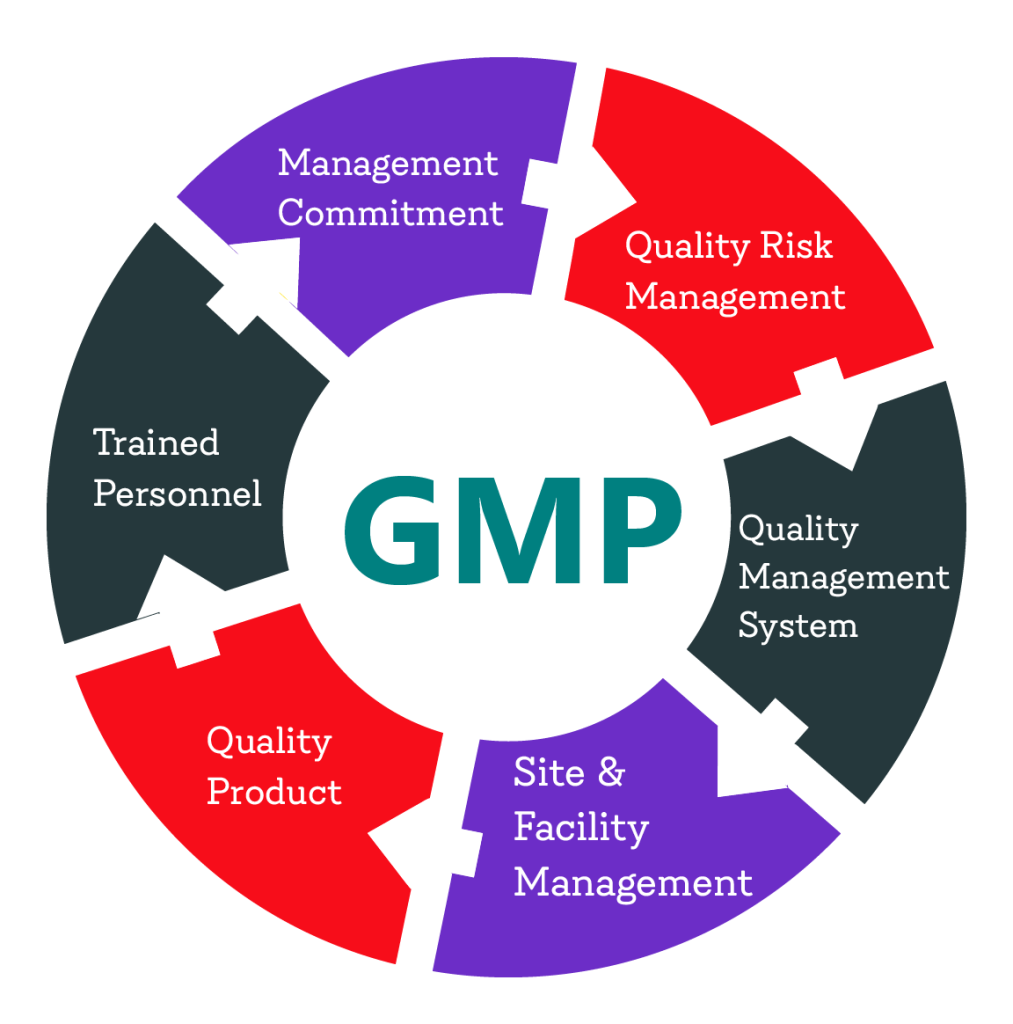
Key aspects
Quality Management System
GMP requires companies to establish and maintain a robust quality management system (QMS) that covers all aspects of production, including personnel, facilities, equipment, materials, processes, and documentation. The QMS should ensure that products are manufactured consistently and meet quality standards.
Facility and Equipment
GMP regulations specify requirements for the design, construction, maintenance, and sanitation of manufacturing facilities and equipment. Facilities must be suitable for their intended purpose, and equipment must be properly calibrated, maintained, and cleaned to prevent contamination and ensure product quality.
Personnel Training and Hygiene
GMP mandates that personnel involved in manufacturing undergo appropriate training and have the necessary qualifications, skills, and knowledge to perform their duties effectively. Personnel must adhere to strict hygiene practices to prevent contamination of products.
Raw Materials and Suppliers
GMP requires companies to establish procedures for the procurement, testing, and control of raw materials, ingredients, and components used in production. Suppliers must be evaluated and approved based on their ability to provide materials that meet quality standards.
Documentation and Records
GMP regulations mandate comprehensive documentation and record-keeping practices to ensure traceability, accountability, and transparency throughout the manufacturing process. This includes maintaining records of production processes, testing results, deviations, and corrective actions.
Process Control and Validation
GMP emphasizes the importance of process control and validation to ensure that manufacturing processes are stable, reproducible, and capable of consistently producing products that meet quality specifications. Validation studies are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness and reliability of manufacturing processes.
Quality Control and Testing
GMP requires companies to implement robust quality control measures, including in-process testing, finished product testing, and stability testing, to monitor and verify the quality of products throughout the manufacturing process. Testing should be conducted using validated methods and performed by qualified personnel.
Compliance and Inspections
GMP regulations are enforced by regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), through inspections and audits of manufacturing facilities. Companies must comply with GMP standards and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements to obtain and maintain product approvals and licenses.
Benefits
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and safety of products, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Let’s explore the benefits of adhering to GMP:
- Consistent Quality: GMP ensures that products are consistently produced to meet high-quality standards. This consistency enhances customer satisfaction and trust.
- Safety and Efficacy: By following GMP guidelines, manufacturers can ensure the safety, purity, and effectiveness of their products. This is critical for protecting consumers’ health.
- Risk Mitigation: GMP addresses potential risks such as cross-contamination, adulteration, and mislabeling. Implementing GMP helps prevent costly recalls, errors, and contamination.
- Legal Compliance: Meeting GMP or current GMP (cGMP) standards ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. It helps companies avoid fines, penalties, and legal issues.
- Efficiency and Waste Reduction: Properly documented processes and adherence to GMP minimize waste, reduce losses, and improve overall efficiency.
- Customer Confidence: GMP-certified products instill confidence in consumers, leading to increased sales and brand reputation.

Overall, GMP standards play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of products manufactured in regulated industries. By implementing GMP principles, companies can minimize the risk of product defects, contamination, and adverse events, thereby safeguarding public health and consumer confidence.
Read more:
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT COMMERCIAL INVOICE

